With Flex Databases Pharmacovigilance, you’ll only need one case, and you can add as many languages to it as you want.
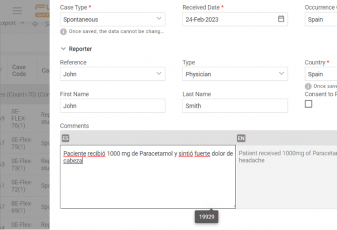
Modern pharmacovigilance, like any other process, in 2021 is impossible without technology and automation. The presence of an electronic system is a guarantee of high-quality and fast collection and processing of safety data. But even with an electronic system in place, it’s not possible to 100% avoid manual labor of collecting and entering data. But it can be minimized, as well as analytics and data exchange can be optimized.
Here’s what you can use for pharmacovigilance automation:
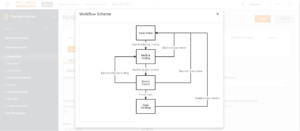
And here’s an overview of possible levels of pharmacovigilance automation:
Basic process automation includes collection of data and metrics, automatic tracking, and task monitoring. When we talk about the pharmacovigilance system’s essential features, it could be, for example, a tool for quality control workflow management, a scientific literature monitoring tool, an urgent submissions tracker, or a calendar for periodic submissions.
Here’s an example from Flex Databases pharmacovigilance system:
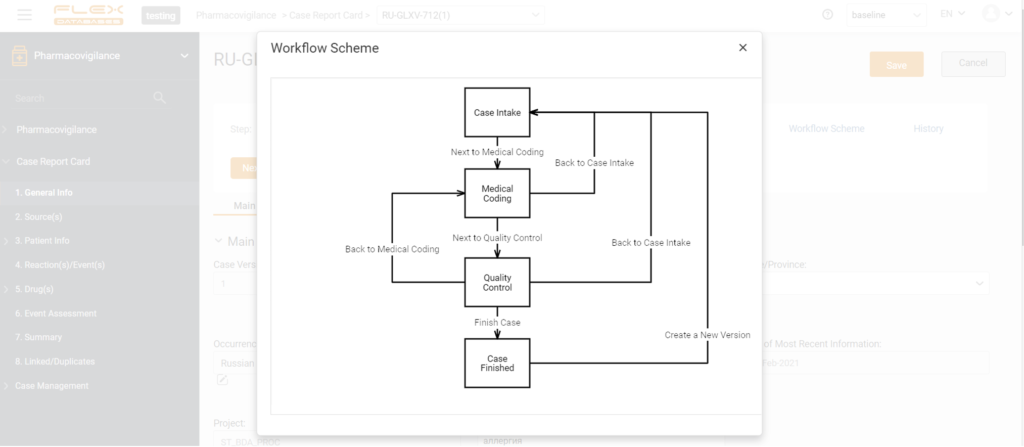
Basic automation allows you to improve the quality of information input, make submissions to the regulatory authorities on time, distribute areas of responsibility among the participants in the process, and receive all the necessary reporting and ensure the collection of metrics.
RPA utilizes special software (bots) to perform manual actions, usually involving repetitive processes. With RPA, you can perform these actions without human intervention or assistance. When applied to an electronic pharmacovigilance system, RPA helps to reduce or virtually eliminate manual labor and leads to automatic data entry, processing, and analysis.
The table below shows examples of similar technologies and potential applications in pharmacovigilance automation:
| Technology | Potential applications in pharmacovigilance automation |
| Natural language generation | Case collection, Periodic reporting, Risk management, Signal management |
| Bots & chat-bots | Case collection, Periodic reporting, Risk management, Signal management, QMS |
| Standalone software | ICSR, aggregate, signal management, risk management, QMS |
Here’s an example of an automated case narrative creation tool from Flex Databases pharmacovigilance system:
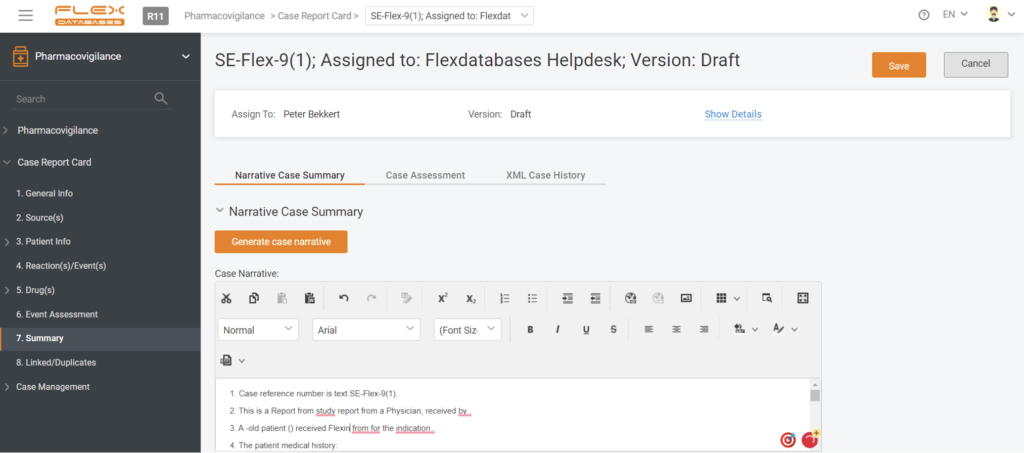
Cognitive automation uses automatic natural language processing (NLP) to help people make decisions and is often combined with RPA.
Here are a few examples:
| Technology | Potential applications in pharmacovigilance automation |
| Optical Character Recognition | Case collection |
| Natural Language Processing | Case collection, Periodic reporting, Signal Management |
| Machine translation | Case collection, Periodic reporting, Risk Management |
| Speech recognition (speech to text) | Case collection |
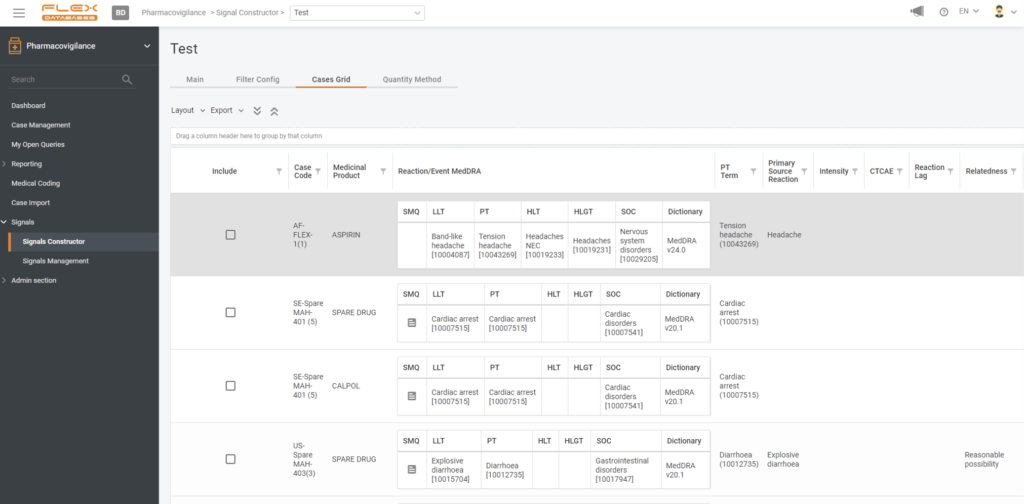
Artificial intelligence encompasses a wide range of technologies, including rule-following, reasoning (using rules to reach rough or specific conclusions), learning, and self-correction. For example, in the Flex Databases system, an AI, based on a neural network, is used to detect and manage signals, find duplicates, and auto-code.
Here’s an example from our system:
To automate pharmacovigilance processes successfully, it is not enough to choose any software provider. You need to decide on the tasks that automation should solve and build the decision on the functional and regulatory compliance of the selected system. Flex Databases’ pharmacovigilance automation system is one of the most functional on the market and fully complies with all local and international regulations.
Want to know more about our system? Order a demo through the form in the header of the page or send us a request to bd@flexdatabases.com
We are here for all of your questions! Tell us more about yourself and we will organize a tailored live demo to show how you can power up your clinical trials processes with Flex Databases.